angstromCTF 2024
Last edited: Mar 2, 2026
https://ctftime.org/event/2375
CHALL’S SOLVED
| Category | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Reverse Engineering | Guess the Flag |
| Reverse Engineering | switcher |
| Web | spinner |
Reverse Engineering
Guess the Flag
Overview
Author: rous
Description: Do you have what it takes to guess the flag? Find out here
Decompiled of the main function
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
char *v3; // rbx
char _0[72]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp+0h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 vars48; // [rsp+48h] [rbp+48h]
vars48 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
puts("Go ahead, guess the flag: ");
v3 = _0;
fgets(_0, 63, stdin);
while ( strlen(_0) > v3 - _0 )
*v3++ ^= 1u;
if ( !strcmp(_0, secretcode) )
puts("Correct! It was kinda obvious tbh.");
else
puts("Wrong. Not sure why you'd think it'd be that.");
return 0;
}From the decompiled code is a simple program that reads a string, applies a bitwise XOR operation to each character in the string and then compares the result to a secretcode.
The XOR operation being applied *v3++ ^= 1u; which flips the least significant bit of each character in the input.
.data:0000000000004020 secretcode db '`bugzbnllhuude^un^uid^md`ru^rhfohghb`ou^chu|',0The secretcode from .data section is 'bugzbnllhuude^un^uid^mdru^rhfohghbou^chu|.
Here’s the final solver
1secret_code = '`bugzbnllhuude^un^uid^md`ru^rhfohghb`ou^chu|'
2original_input = ''.join(chr(ord(c) ^ 1) for c in secret_code)
3print(original_input)$ python3 solver.py
actf{committed_to_the_least_significant_bit}FLAG
actf{committed_to_the_least_significant_bit}
switcher
Overview
Author: aplet123
Description: It’s incredible how completely indiscernible the functions are…
Decompiled of the sub_5540 function
void __fastcall sub_5540(_BYTE *a1)
{
_BYTE *v1; // rdi
_BYTE *v2; // rdi
_BYTE *v3; // rdi
_BYTE *v4; // rdi
_BYTE *v5; // rdi
_BYTE *v6; // rdi
_BYTE *v7; // rdi
_BYTE *v8; // rdi
_BYTE *v9; // rdi
_BYTE *v10; // rdi
_BYTE *v11; // rdi
_BYTE *v12; // rdi
_BYTE *v13; // rdi
_BYTE *v14; // rdi
_BYTE *v15; // rdi
_BYTE *v16; // rdi
_BYTE *v17; // rdi
_BYTE *v18; // rdi
_BYTE *v19; // rdi
_BYTE *v20; // rdi
_BYTE *v21; // rdi
_BYTE *v22; // rdi
_BYTE *v23; // rdi
_BYTE *v24; // rdi
_BYTE *v25; // rdi
_BYTE *v26; // rdi
_BYTE *v27; // rdi
_BYTE *v28; // rdi
_BYTE *v29; // rdi
_BYTE *v30; // rdi
_BYTE *v31; // rdi
_BYTE *v32; // rdi
_BYTE *v33; // rdi
_BYTE *v34; // rdi
_BYTE *v35; // rdi
_BYTE *v36; // rdi
if ( *a1 == 106 )
{
v36 = a1 + 1;
if ( *v36 == 117 )
{
v35 = v36 + 1;
if ( *v35 == 109 )
{
v34 = v35 + 1;
if ( *v34 == 112 )
{
v33 = v34 + 1;
if ( *v33 == 105 )
{
v32 = v33 + 1;
if ( *v32 == 110 )
{
v31 = v32 + 1;
if ( *v31 == 103 )
{
v30 = v31 + 1;
if ( *v30 == 95 )
{
v29 = v30 + 1;
if ( *v29 == 109 )
{
v28 = v29 + 1;
if ( *v28 == 121 )
{
v27 = v28 + 1;
if ( *v27 == 95 )
{
v26 = v27 + 1;
if ( *v26 == 119 )
{
v25 = v26 + 1;
if ( *v25 == 97 )
{
v24 = v25 + 1;
if ( *v24 == 121 )
{
v23 = v24 + 1;
if ( *v23 == 95 )
{
v22 = v23 + 1;
if ( *v22 == 116 )
{
v21 = v22 + 1;
if ( *v21 == 111 )
{
v20 = v21 + 1;
if ( *v20 == 95 )
{
v19 = v20 + 1;
if ( *v19 == 116 )
{
v18 = v19 + 1;
if ( *v18 == 104 )
{
v17 = v18 + 1;
if ( *v17 == 101 )
{
v16 = v17 + 1;
if ( *v16 == 95 )
{
v15 = v16 + 1;
if ( *v15 == 102 )
{
v14 = v15 + 1;
if ( *v14 == 108 )
{
v13 = v14 + 1;
if ( *v13 == 97 )
{
v12 = v13 + 1;
if ( *v12 == 103 )
{
v11 = v12 + 1;
if ( *v11 == 95 )
{
v10 = v11 + 1;
if ( *v10 == 111 )
{
v9 = v10 + 1;
if ( *v9 == 110 )
{
v8 = v9 + 1;
if ( *v8 == 101 )
{
v7 = v8 + 1;
if ( *v7 == 95 )
{
v6 = v7 + 1;
if ( *v6 == 98 )
{
v5 = v6 + 1;
if ( *v5 == 121 )
{
v4 = v5 + 1;
if ( *v4 == 95 )
{
v3 = v4 + 1;
if ( *v3 == 111 )
{
v2 = v3 + 1;
if ( *v2 == 110 )
{
v1 = v2 + 1;
if ( *v1 == 101 )
sub_1200(v1 + 1);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}The sub_5540 function checks if the input string matches a specific sequence of ASCII characters. Each if statement checks if the current character equals a specific ASCII value, and if it does, it moves to the next character. If all checks pass, it calls the sub_1200 function.
The ASCII values in the if statements correspond to the following characters:
106 -> 'j'
117 -> 'u'
109 -> 'm'
112 -> 'p'
105 -> 'i'
110 -> 'n'
103 -> 'g'
95 -> '_'
109 -> 'm'
121 -> 'y'
...
101 -> 'e'Final solver
1flag = [106, 117, 109, 112, 105, 110, 103, 95, 109, 121, 95, 119, 97, 121, 95, 116, 111, 95, 116, 104, 101, 95, 102, 108, 97, 103, 95, 111, 110, 101, 95, 98, 121, 95, 111, 110, 101]
2dec = ''.join(chr(i) for i in flag)
3print(f'actf{{{dec}}}')$ python3 solver.py
actf{jumping_my_way_to_the_flag_one_by_one}FLAG
actf{jumping_my_way_to_the_flag_one_by_one}
Web
spinner
Move on to 1 web challenge that I only solved, the web provided spins a spinner and once the total rotation reaches 10,000 full spins.
However, manually spinning this to reach 10,000 full spins would be quite time-consuming and impractical. Instead, we can manipulate the JavaScript code to reach the required total spins instantly.
<script>
const state = {
dragging: false,
value: 0,
total: 0,
flagged: false,
}
const message = async () => {
if (state.flagged) return
const element = document.querySelector('.message')
element.textContent = Math.floor(state.total / 360)
if (state.total >= 10_000 * 360) {
state.flagged = true
const response = await fetch('/falg', { method: 'POST' })
element.textContent = await response.text()
}
}
message()
const draw = () => {
const spinner = document.querySelector('.spinner')
const degrees = state.value
spinner.style.transform = `rotate(${degrees}deg)`
}
const down = () => {
state.dragging = true
}
const move = (e) => {
if (!state.dragging) return
const spinner = document.querySelector('.spinner')
const center = {
x: spinner.offsetLeft + spinner.offsetWidth / 2,
y: spinner.offsetTop + spinner.offsetHeight / 2,
}
const dy = e.clientY - center.y
const dx = e.clientX - center.x
const angle = (Math.atan2(dy, dx) * 180) / Math.PI
const value = angle < 0 ? 360 + angle : angle
const change = value - state.value
if (0 < change && change < 180) state.total += change
if (0 > change && change > -180) state.total += change
if (change > 180) state.total -= 360 - change
if (change < -180) state.total += 360 + change
state.value = value
draw()
message()
}
const up = () => {
state.dragging = false
}
document.querySelector('.handle').addEventListener('mousedown', down)
window.addEventListener('mousemove', move)
window.addEventListener('mouseup', up)
window.addEventListener('blur', up)
window.addEventListener('mouseleave', up)
</script>From the JavaScript source-code, the total rotation reaches 10,000 full spins (360 degrees * 10,000), it makes a POST request to the /falg endpoint to get the flag.
The simple way to do it using the browser’s JavaScript console that set the total spins to the required value and then call the message function to update the total and fetch the flag
state.total = 10_000 * 360;
message();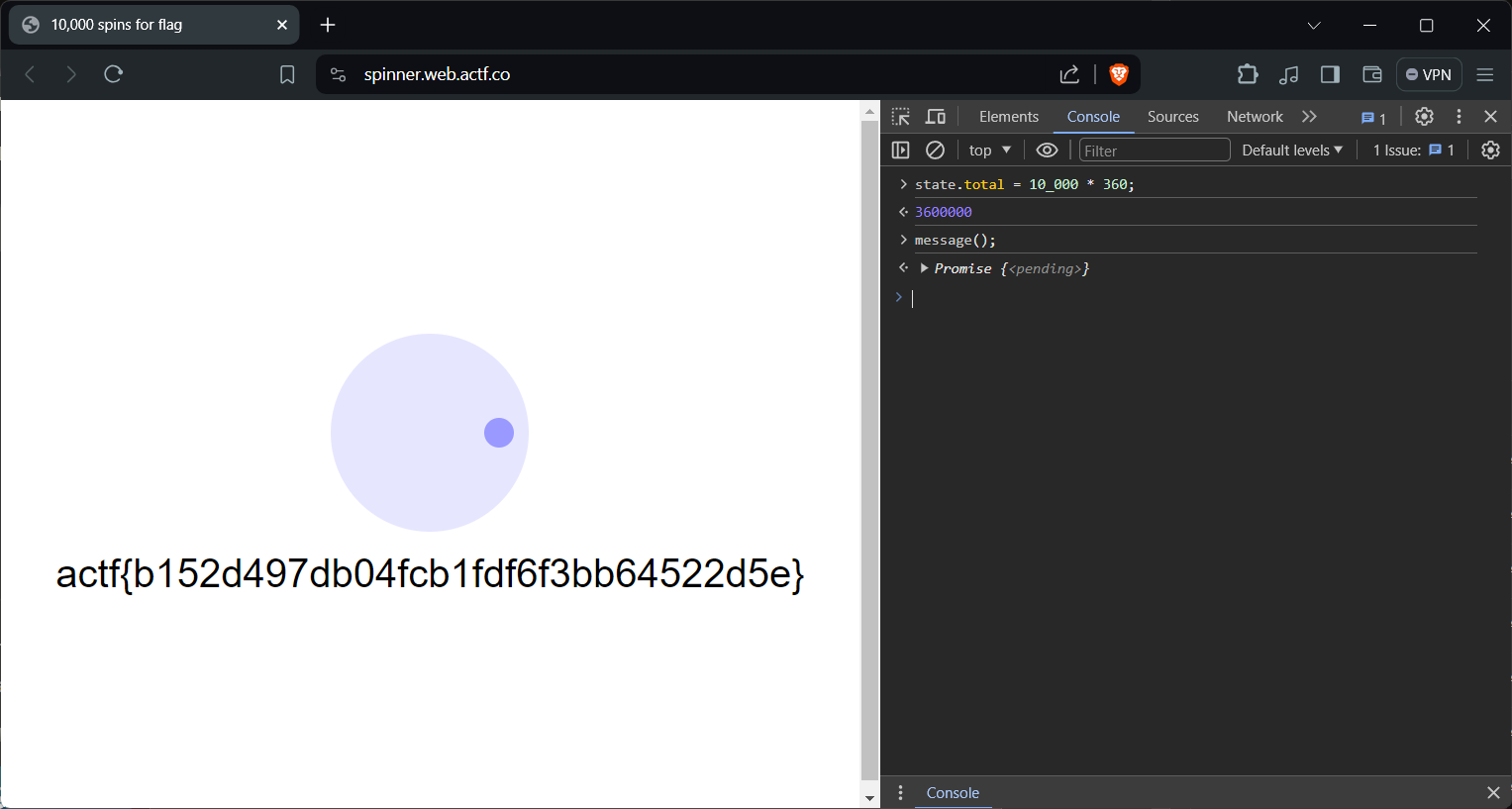
Final solver using python
1import requests
2
3url = 'https://spinner.web.actf.co'
4endpoint = '/falg'
5
6response = requests.post(url + endpoint)
7
8print(response.text)$ python3 solver.py
actf{b152d497db04fcb1fdf6f3bb64522d5e}FLAG
actf{b152d497db04fcb1fdf6f3bb64522d5e}
